Heart attacks and sudden cardiac arrest are very serious medical emergencies that require immediate attention and often require life-long health adjustments and treatments.
Learning basic life support is a critical way to properly handle these situations when they arise. But it’s even better to prevent them from happening altogether.
Heart disease may be the leading cause of death in the United States, but it doesn’t have to be that way. There are several steps that you can take to ensure you don’t suffer a cardiac emergency.
What is a Cardiac Emergency?
A cardiac emergency can be one of two things:
- Heart attack
- Sudden cardiac arrest
These two emergency situations are often misconstrued as being the same thing. However, they are two different health conditions.
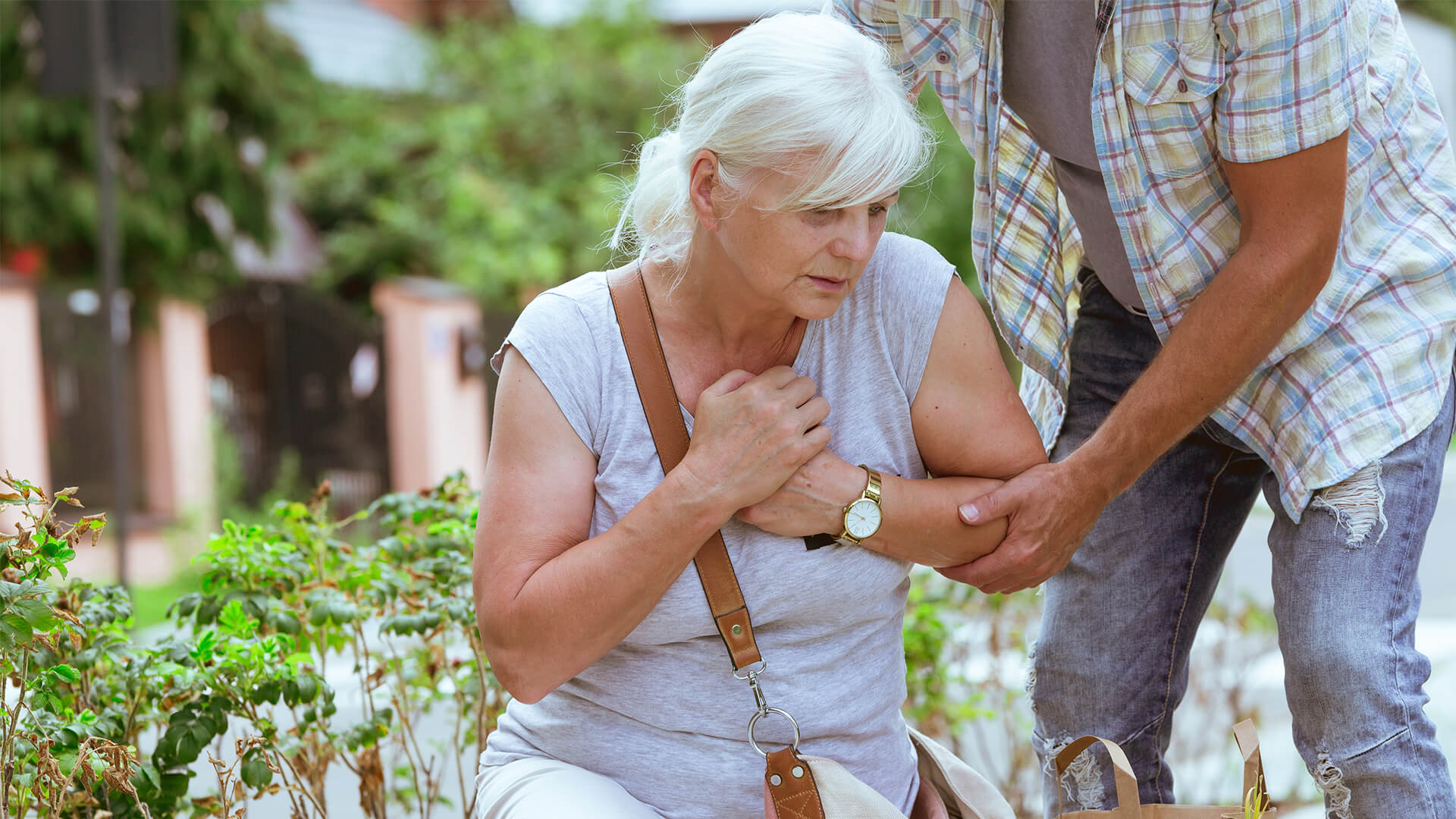
A heart attack (or myocardial infarction), occurs when the blood flow to the heart is either reduced or cut off completely. This situation can take place due to a blood clot or a spasm of the coronary artery.
Someone experiencing a heart attack may feel a sudden, intense pain in the chest that can spread to the arms, shoulders, jaw, and neck. They may also feel dizzy, nauseous, and overly tired with symptoms that include sweating, heartburn, and difficulty breathing.
On the other hand, sudden cardiac arrest means that the heart has suddenly become paralyzed. The rest of an individual’s organs cannot receive blood and oxygen at that time.
Sudden cardiac arrest happens very quickly, resulting in asystole. Someone experiencing sudden cardiac arrest will immediately faint and lose consciousness. A heart attack can lead to sudden cardiac arrest if not treated quickly.
How to Reduce the Risk of a Cardiac Emergency
There are certain factors that we can’t change, such as family health history, age, and sex. However, we can take action to improve our overall health, therefore mitigating the risk of cardiac arrest in the future.
Do Not Smoke or Use Tobacco
The chemicals found in tobacco can be severely damaging to both your heart and your blood vessels. In fact, smoking cigarettes causes about 1 in every 5 deaths in the U.S. every year.
These chemicals can significantly increase your risk of atherosclerosis, a condition that causes plaque to build up in the arteries. This plaque progressively hardens and narrows the arteries, limiting the flow of blood and oxygen throughout the body.
The continual buildup of this plaque can eventually lead to heart attack and heart failure as it blocks the blood supply to the heart and the coronary arteries over time.
Studies show that your risk of heart disease begins to lower the day you quit smoking and tobacco use. So, even if you’ve smoked for a long time, stopping at any point can still benefit your heart health.
Exercise Regularly
The CDC recommends that adults should get at least 150 minutes of exercise per week, which breaks down to 30 minutes for five days each week. They also state that adults should move more and sit less during the day, keeping their bodies active rather than sedentary for long periods of time.
But what does this have to do with heart disease?
Consistent physical activity plays an important role in maintaining a healthy heart. Since the heart is a muscle, it needs exercise as much as the rest of your body. Physical activity can help control your weight and minimizes the risk of developing conditions such as:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Type 2 diabetes
These conditions can all put a strain on your heart and lead to additional heart problems and cardiac emergencies. Even small amounts of exercise, such as a short walk or cleaning your house, can improve your heart health.
Healthy Diet
Maintaining a healthy diet can have several benefits, such as preventing stroke, diabetes, and obesity. Eating healthy foods and managing your nutritional intake can also prevent long-term heart disease.
A healthy diet involves finding a good balance among nutrients, which is generally achievable by balancing the main food groups:
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Milk and Dairy
- Protein
Another food group includes fatty and sugary foods. While it’s not necessary to avoid these foods completely, they should only make up a very small portion of your daily intake. Too much fat and sugar can lead to weight gain, which can ultimately cause stroke, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
Improve Sleep Quality
Constant lack of sleep can be detrimental to your overall health, including that of your heart. Most adults should get at least seven hours of sleep every night. Those who don’t achieve this amount of sleep are at higher risk for high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart attack.
When you sleep, your heart rate slows and your blood pressure drops down. This is considered a normal part of your sleep cycle and is the much-needed rest that your body needs to survive and thrive. But when you don’t get enough sleep, your blood pressure stays higher for a longer amount of time.
Therefore, not getting enough sleep can lead to high blood pressure down the line. High blood pressure is a leading risk for heart disease and stroke.
Conclusion
Cardiac emergencies are very real and life-threatening health conditions that impact thousands of people every year. The best thing you can do for yourself is to take proactive steps toward improving your overall health. Staying healthy, active, and well-rested can provide a great foundation for good heart health.