It’s no secret that what we eat profoundly affects our overall health, including our hearts’ health. Unfortunately, the typical Western diet heavy on processed foods, saturated fats, and refined sugars is doing us no favours regarding heart health. On the other hand, researchers agree that a plant-based diet can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular problems.
Tip 1: Go for Whole, Nutrient-Dense Foods
First and foremost, remember that eating healthily is all about motivation. If you’re looking for inspiration to incorporate these whole, nutrient-dense foods into your diet, a moodboard can be a helpful tool. The best part about it? You can easily find moodboard template free of charge, so you don’t have to be a graphic designer and spend hours just to get started.
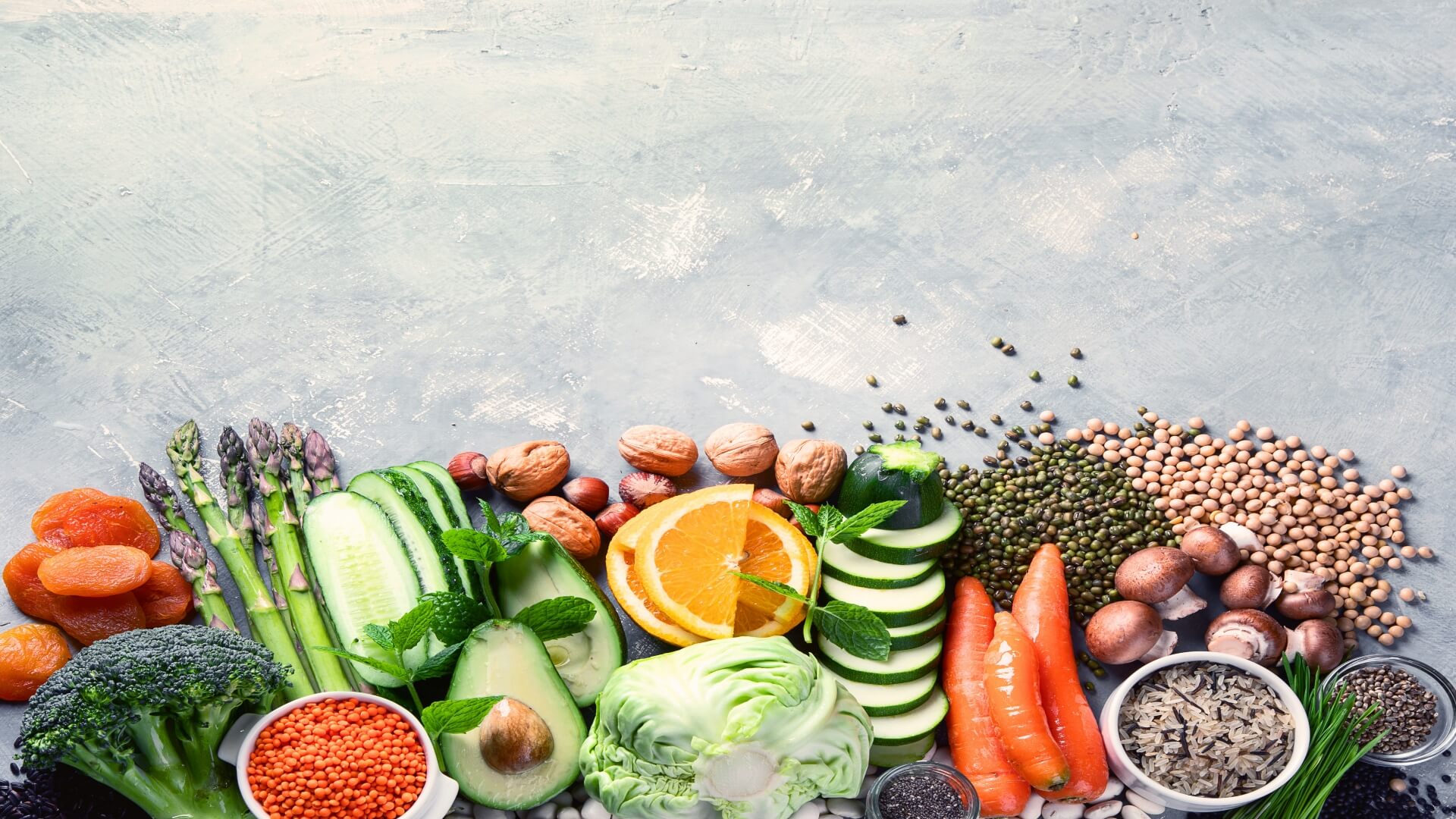
So what are the go-to nutrition-packed foods to eat in the first place? Leafy greens, of course! Vegetables like spinach and kale are packed with vitamins A, C, and K and minerals like iron and calcium. These nutrients have been shown to help reduce inflammation, lower blood pressure, and improve overall heart health.
Tip 2: Prioritize Plant-Based Protein Sources
Protein is essential for our overall health, as it helps build and repair tissues and supports the production of vital enzymes and hormones. Regarding heart health and a plant-based diet, prioritize high-quality protein sources that are nutrient-dense and low in saturated fats.
Fortunately, there are plenty of palatable and nutritious protein sources. Tofu, tempeh, beans, and legumes are all excellent choices for those looking to support their heart health.
For example, black beans help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease, while tempeh is a good source of protein and probiotics that can support a healthy gut microbiome. Tofu is another popular protein source rich in calcium, iron, and magnesium.
Tip 3: Incorporate Healthy Fats into Your Diet
Remember that not all fats are created equal. While it’s true that saturated and trans fats can increase the risk of heart disease, healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and seeds can be instrumental for our cardiovascular system.
Use some smashed avocado as a sandwich spread, or add walnuts to your morning oatmeal for a dose of healthy fats. You can also snack on a handful of almonds or pumpkin seeds for a satisfying and nutrient-rich snack.
It’s important to note that while healthy fats are beneficial for heart health, they are still high in calories and should be consumed in moderation as part of a well-balanced diet.
Tip 4: Avoid Processed and High-Fat Foods to Support Heart Health
Processed and high-fat foods are debilitating and greatly contribute to heart disease. These foods often contain extremely high levels of saturated fats and empty calories, which can lead to rapid weight gain, high cholesterol, and other risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
To reduce your consumption of such foods, start by reading food labels and staying away from foods high in saturated and trans fats, added sugars, and sodium. Instead, opt for more nutritious snacks like air-popped popcorn, fresh fruits and vegetables, or flavoured seltzer instead of soda to satisfy your cravings.
Tip 5: Address Nutrient Deficiencies to Support Heart Health
While a plant-based diet can offer many health benefits, be mindful of potential nutrient deficiencies. Some nutrients essential for heart health, such as vitamin B12, iron, and calcium, can be harder to obtain from a strictly meatless diet.
Vitamin B12 is necessary for forming red blood cells and proper nerve function. It is primarily found in animal products, so those on a meat-free diet may need to supplement with vitamin B12 or consume fortified foods such as plant-based milk, cereals, and nutritional yeast.
Iron is essential for carrying oxygen to the body’s cells, and plant-based sources of iron are less easily absorbed than those from animal products. Increase absorption by consuming iron-rich foods with vitamin C sources, such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, and bell peppers. Plant-based iron sources include leafy greens, beans, lentils, tofu, and fortified cereals.
Calcium is vital for building and maintaining strong bones and also plays a role in heart health. While dairy products are a rich source of calcium, there are many plant-based sources of this nutrient, including leafy greens, almonds, and fortified plant-based milk.
Wrapping Up
In a nutshell, a plant-based diet can do wonders for your heart health. Say goodbye to the greasy burgers and hello to the nutrient-packed goodness of leafy greens, protein-packed beans and legumes, and heart-healthy fats from avocados and nuts. Cut back on the processed junk and give your taste buds a twist. Wait no longer! Let’s get cracking on some deliciousness and give your heart some love!